Polyprotic acids and bases dissociation constants
First, and the simplest approach to defining equilibriums constants for polyprotic acid is to treat every step of dissociation separately:
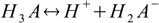
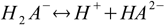
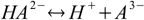
Then we have three stepwise dissociation constants:
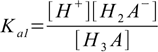 3.1
3.1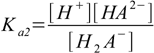 3.2
3.2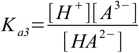 3.3
3.3There are also overall dissociation constants defined, of which first is identical to the stepwise one, while the second and the third take forms:
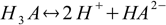
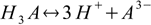
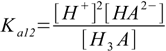 3.4
3.4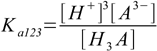 3.5
3.5It is not very difficult to find out relations:
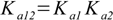 3.6
3.6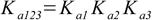 3.7
3.7or
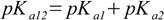 3.8
3.8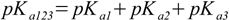 3.9
3.9For polyprotic acids with greater number of protons analogous constants are used.
Same holds for polyprotic bases.
In case of polyprotic substances the idea of conjugate acids and bases becomes a little bit confusing, as the same substance can play both roles:
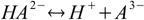 acid
acid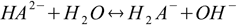 base
baseand the numeration of dissociation steps is reversed, so that first acid dissociation step described by Ka1:
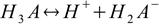
creates conjugate base for the last dissociation step:
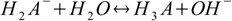
described by Kb3. So for the substance with three protons relations analogous to 2.5 take forms:
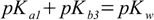 3.10
3.10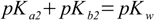 3.11
3.11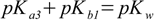 3.12
3.12


